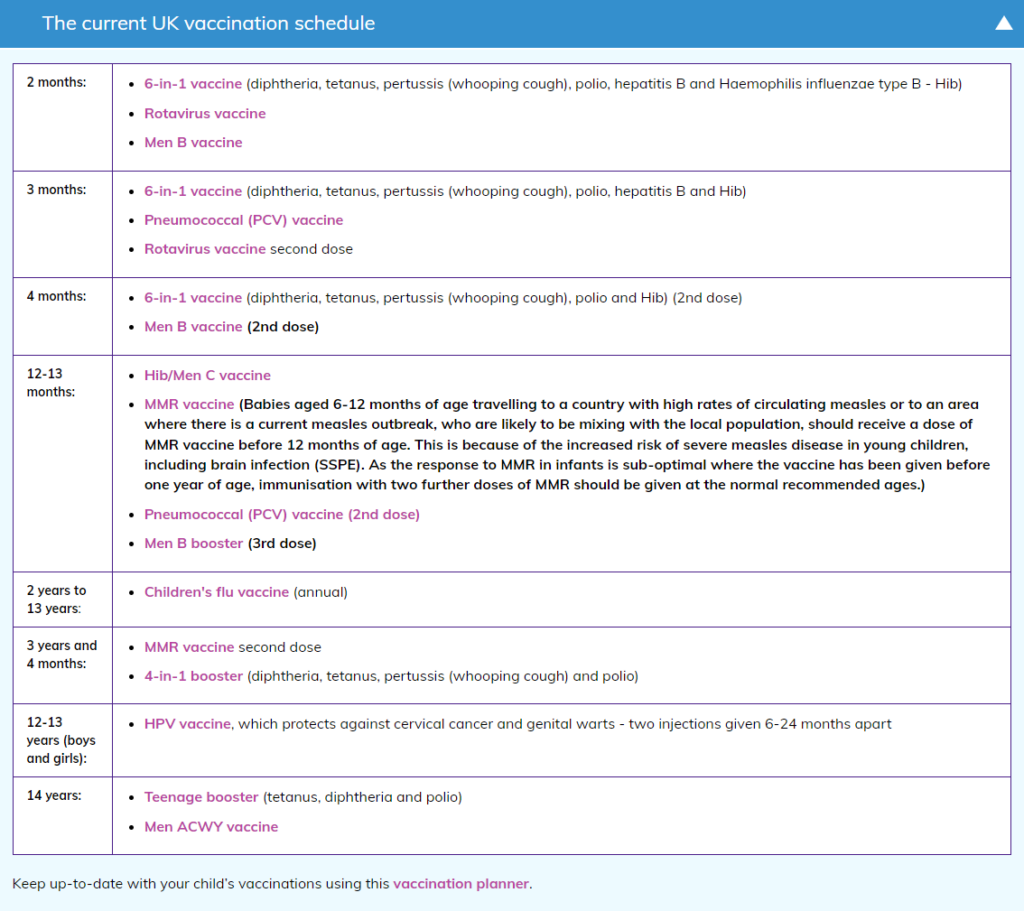
Routine immunisations are given to children before they start school to help protect them from serious childhood diseases.
To find out more
Flu vaccine

Measles
HPV

Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the name of a very common group of viruses. They do not cause any problems in most people, but some types can cause genital warts or cancer.
Teenage Booster and MenACWY

The teenage booster, also known as the 3-in-1 or the Td/IPV vaccine, is given to boost protection against 3 separate diseases: tetanus, diphtheria and polio.
The MenACWY vaccine is given by a single injection into the upper arm and protects against 4 strains of the meningococcal bacteria – A, C, W and Y – which cause meningitis and blood poisoning (septicaemia).
COVID





